

Can one pupil be more dilated than the other? If pupils dilate suddenly, occur after a traumatic injury or cause headaches and confusion, seek medical attention immediately. Most of the time, dilated pupils will go back to normal size on their own. Pupils are supposed to dilate under normal circumstances due to light changes and emotional variables. Should I be worried about my dilated pupils? Pupils are dilated when the center black portion of your eyes takes up more space than the colorful portion of your eyes (iris). Another term for mydriasis is “fixed pupil.” What is a normal size for pupils?Ī pupil’s normal size is 2 to 4 millimeters in bright light and 4 to 8 millimeters in dim light (dilated). Mydriasis is when the pupil is dilated and doesn’t respond to light. If a pupil does not get smaller in bright light or expand in the dark, the pupil is not functioning normally. This is called an accommodative response. Pupils also shrink when you focused on a close object. These changes are called direct responses. In the dark, pupils get larger to allow more light in.
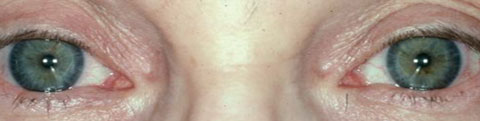

In bright light, your pupils will get smaller to prevent light from entering. The colorful part of your eye (iris) controls the size of your pupil with tiny muscles. Pupils change in size to control how much light enters your eye. Pupils are typically the same size in both eyes. If your pupils are dilated, the black center of your eyes (pupils) are larger than usual. When it gets darker, your pupils dilate (get bigger) to let in more light. When you're outside in the sunlight or in a brightly lit room, your pupils constrict (get smaller).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
